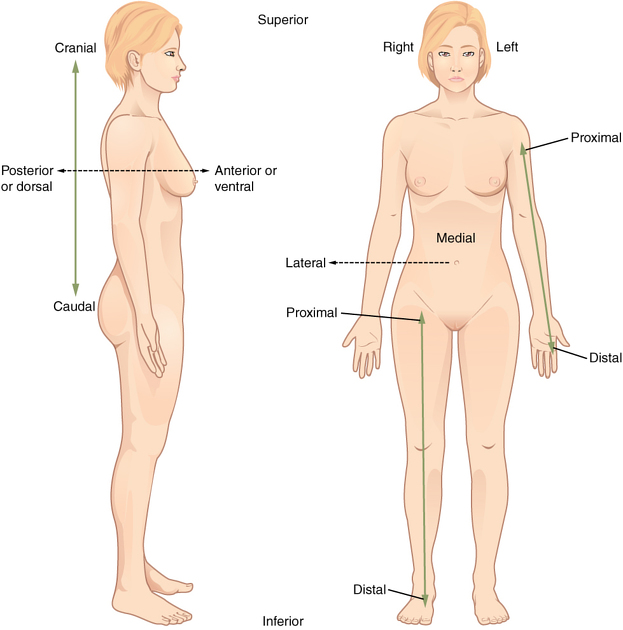
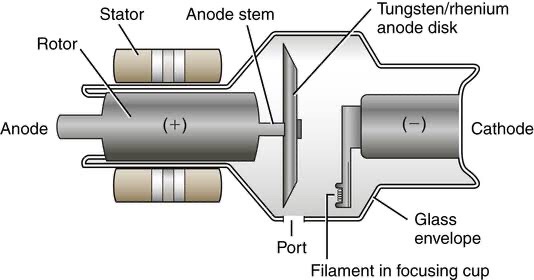
This is used to describe the position of the patient for taking various radiographs. Standard nomenclature is employed with respect to the anatomic position.
Basic terms of relations
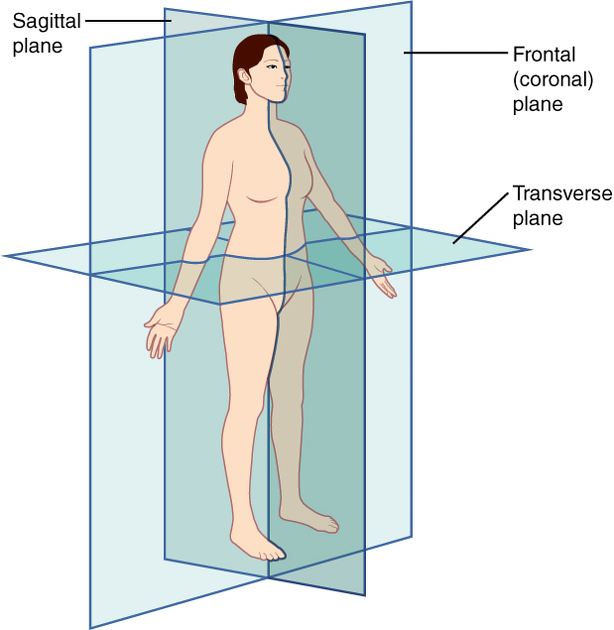
Planes
- the axial plane (transverse or transaxial plane): horizontal plane perpendicular to the long axis of the body
- divides the body into superior and inferior parts
- the sagittal plane: vertical plane parallel to the median plane (or midsagittal plane)
- divides the body into right half and left halves
- the coronal plane: vertical plane perpendicular to the median plane
- divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
BODY POSITION
- Erect: either standing or sitting
- Decubitus: lying down
- Supine: lying on back
- Trendelenburg position: the patient is supine (on an inclined radiographic table) with the head lower than the feet
- Prone: lying face-down
- Lateral decubitus: lying on one side
- right lateral: right side touches the cassette
- left lateral: left side touches the cassette
Movement
- flexion: decrease in the angle of the joint
- extension: increase in the angle of the joint
- abduction: movement of limb away from midline
- adduction: movement of limb towards the midline
- pronation: movement of hand and forearm to bring the palm facing posterior
- supination: movement of hand and forearm to bring the palm facing anterior
- circumduction: circular movement of a joint using a combination of flexion, abduction, extension and adduction such that the distal limb describes a circle
- opposition: thumb brought to oppose another digit
- reposition: thumb repositioned back to the anatomic position
- elevation: movement of the scapular superiorly
- depression: movement of the scapular inferiorly
- eversion: movement of the sole of the foot away from the median plane
- inversion: movement of the sole of the foot towards from the median plane
- protrusion: movement of the mandible, lips or tongue anteriorly
- retraction: movement of the mandible, lips or tongue posteriorly
Projections
- antero-posterior (AP): central ray passes, perpendicular to the coronal plane, from anterior to posterior
- postero-anterior (PA): central ray passes, perpendicular to the coronal plane, from posterior to anterior
- depending on the anatomic segment to radiograph, synonyms can be used, for example: occipito-frontal (skull); dorso-ventral (thorax); dorso-palmar (hand)
- lateral: central ray, perpendicular to the sagittal plane and parallel to the coronal plane, passes from one side of body to the other
- oblique: central ray passes through the body/body part through a plane which is at an angle to the transverse plane/coronal plane
- axial: central ray passes through (or parallel) to the long axis of the body
- in some cases, however, the central ray runs through (or parallel) to the long axis of the skeletal segment studied (for example, the axial view of the calcaneus)